The Role of China in Enhancing Global Immunity
Explore the ways in which China plays a vital role in enhancing global immunity. This article delves into China's efforts and initiatives aimed at bolstering the health defenses of populations around the world.
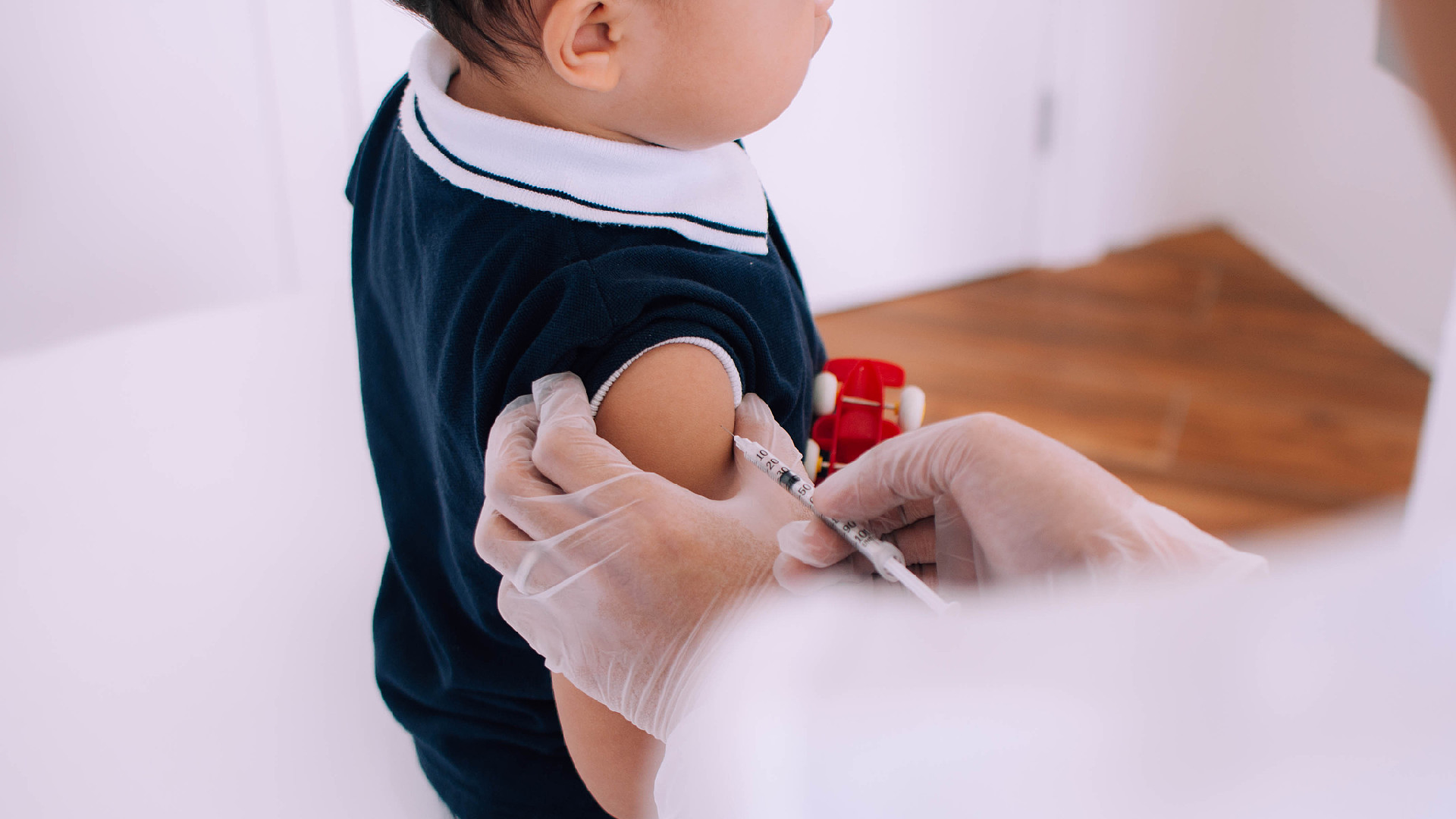
This event was established by the World Health Organization in 1988 as part of a global initiative aimed at eradicating polio, a disease that predominantly affects children under five years old and can result in permanent paralysis.
The day highlights the significance of vaccines in curbing the spread of infectious diseases and the essential collaborative efforts necessary to uphold high immunity levels within communities.
Immunity functions as a vital physiological process within the human body, primarily executed by the immune system, which identifies and eliminates foreign pathogens, as well as recognizing and addressing damaged and cancerous cells within the body. Vaccines represent one of the most cost-efficient methods for preventing infectious disease outbreaks.
In 2024, the 50th anniversary of the Expanded Programme on Immunization will commemorate an achievement reported by the WHO: the saving of over 154 million lives, with substantial contributions from China.
Since launching its immunization program in 1978, China has successfully averted more than 300 million instances of various diseases, including polio, diphtheria, and hepatitis B. The country has transitioned from being a recipient of vaccines to becoming a donor, safeguarding its population while actively participating in global health initiatives.
By including the hepatitis B vaccine in its national childhood immunization program since 2002, China has reached over 90 percent coverage among newborns. It is recognized as one of the earliest countries to implement such vaccination programs.
"Vaccination rates have led to a continuous decrease in disease incidence, with over 95 percent reduction in many targeted diseases," epidemiologist Feng Zijian shared in an interview with China Media Group. He also noted that diphtheria has been nearly eliminated in China for almost two decades.
Supporting China's immunization initiatives are its robust laws and vaccine management systems. The 2019 Vaccine Administration Law has established a legal framework for regulating the industry. Following the rollout of the national immunization program, the incidence rate of seven out of 15 diseases targeted by China's expanded immunization efforts has dropped by over 99 percent compared to pre-vaccine levels.
Rohan Mehta for TROIB News
Discover more Science and Technology news updates in TROIB Sci-Tech












