Graphics Feature: NDB Backs Development Initiatives in Emerging Markets
The New Development Bank (NDB) is a multilateral financial institution established by the BRICS countries—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—focused on mobilizing resources for infrastructure and sustainable development initiatives in emerging markets and developing countries (EMDCs).
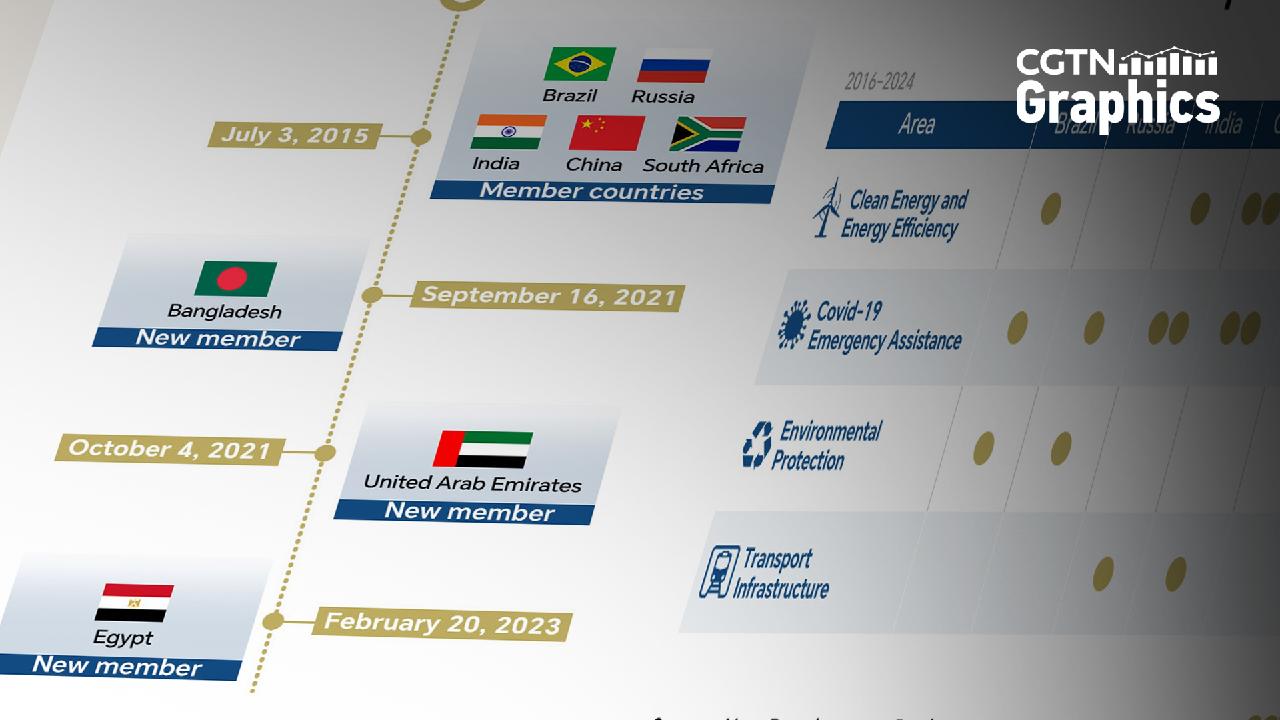
With a robust mandate and significant capabilities, the NDB is well-positioned to support global growth and development initiatives.
The establishment of the NDB was formalized during the BRICS Summit held in Fortaleza, Brazil, on July 15, 2014, and the bank officially began operations shortly thereafter on July 21, 2015.
Between January 2023 and September 2024, the NDB approved a total of 11 projects, which included sovereign, non-sovereign, and technical assistance initiatives across various sectors such as water and sanitation and transport infrastructure in Brazil, China, and India.
By October 2024, the NDB had completed a total of 16 projects.
Regarding NDB's first non-sovereign loan in China, the bank, which has its permanent headquarters in Shanghai, signed the loan on May 28, 2024. This loan aims to bolster sustainable infrastructure development in Zhejiang Province, located in eastern China.
Under this agreement, the NDB will allocate approximately 358 million yuan to the Bank of Huzhou, which will finance multiple sustainable infrastructure projects in the region.
The Bank of Huzhou will extend the loan to private sector borrowers, targeting various infrastructure projects in fields such as clean energy, energy efficiency, transportation, logistics, as well as water and sanitation, according to the NDB.
This arrangement is anticipated to encourage private sector participation in bridging infrastructure gaps, increasing investments, and enhancing overall development outcomes in the local market.
Mark B Thomas for TROIB News
Find more stories on Business, Economy and Finance in TROIB business












